Allows a task to iterate through the values of the results of an SQL query. For example, you might create a task that connects to the company human resources database and queries for all records of employee sick leave reports every month and saves a report to a file.
Important
•You must be familiar with SQL syntax to use this action.
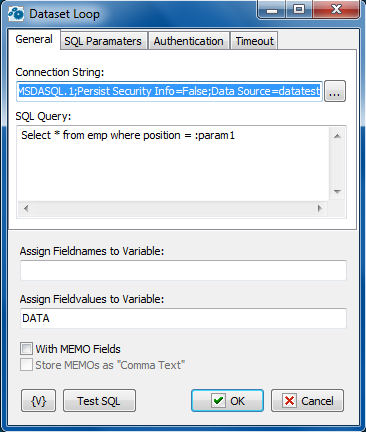
Connection String
A string with attribute/value pairs for information required to log on to a database and point to a specific database. Click the browse button to open the Microsoft Data Link Properties dialog box. You can press F1 to access Help about this dialog box.
SQL Query
Enter the query string in SQL syntax.
Assign Field Names to Variable
Stores the field names separated by commas in a specified variable.
Assign Field Values to Variable
Stores the field values separated by commas in a specified variable.
With Memo Fields
Specifies that the query should include memo fields.
Store Memos as "Comma Text"
Indicates that the memo fields should be stored as comma delimited text.
Test SQL
Allows you to test the SQL syntax of your query.
SQL parameters
Sometimes using of parameters of a query is more convenient instead of generation of the query by means of variables. For example, when the variable value contains quotes or another special symbols. If you use variables (or macro substitution) when forming SQL inquiry, availability such symbols can "break" the syntax of the query and you will get a runtime error.
Parameters SQL are designated in the inquiry by means of colon (:) before the parameter name.
For example:
Select * from employee where hiredate > :dt and salary >= :amount
:dt and :amount are parameters of the query.
Parameters can be several types:
•String – any string
•Integer – an integer number
•Float – a real number or the number with a floating dot.
•Boolean – a logical value True or False.
•DateTime – a date and time. The value of such parameter must be defined in current system format of date and time (see the system regional settings). Notice that using of date-time can have its own characteristics for different databases. For example, it is better specify such parameters for the MySQL as a string parameter in the format YYYY-MM-DD or YYYY-MM-DD hh:nn:ss.
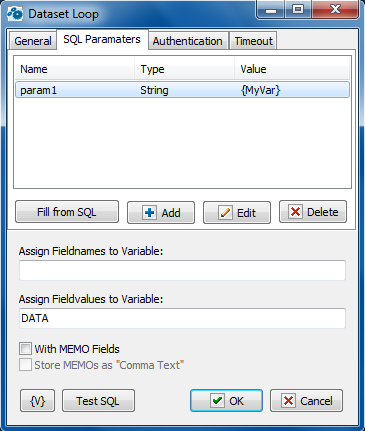
Fill from SQL
Fill the list of parameters from the current query. If a parameter is already in the list, this parameter will be without change. The function fills only the missing parameters in the list.
Add
Add a parameter manually. You will be proposed to type or select from the list the parameter name, select the parameter type and input an expression as the parameter value.
Using of variables in a parameter name and in its value is allowed. The RoboTask will substitute variable values instead of variables before performing the SQL.
Edit
Edit the properties of the selected parameter.
Delete
Delete the selected parameter from the list.
If you specify the parameter which is absent in the query, the action ignores this parameter when performing and writes the proper warning in the log of the task.
Variable
Allows you to add a variable to the action or triggering event that you selected. You must place the cursor in a edit box in the settings dialog window of the action or event and then click the {V} button.
![]() Related Topics
Related Topics