In this chapter, we will look at some recommendations (guidelines) for debugging a generated task. If the task consists of 3-5 consecutive steps, debugging is usually not required. But if the task has more than 30 steps with loops and branches (if ... then ... else), then it probably has hidden errors that are not immediately visible.
Be sure to check the task you have created using the test example.
Without experience, it is difficult to reproduce the entire algorithm in your mind and write it down as a task without errors. It is human nature to make mistakes.
Testing is necessary to verify the functionality and correctness of the task. You can check the implementation of the task, for example, using the files in the test folder or files that can be easily restored from a backup.
The task can only be called after checking that it works correctly. Otherwise, you may damage your working files. Or the task will not work on time, and you will not get the desired result.
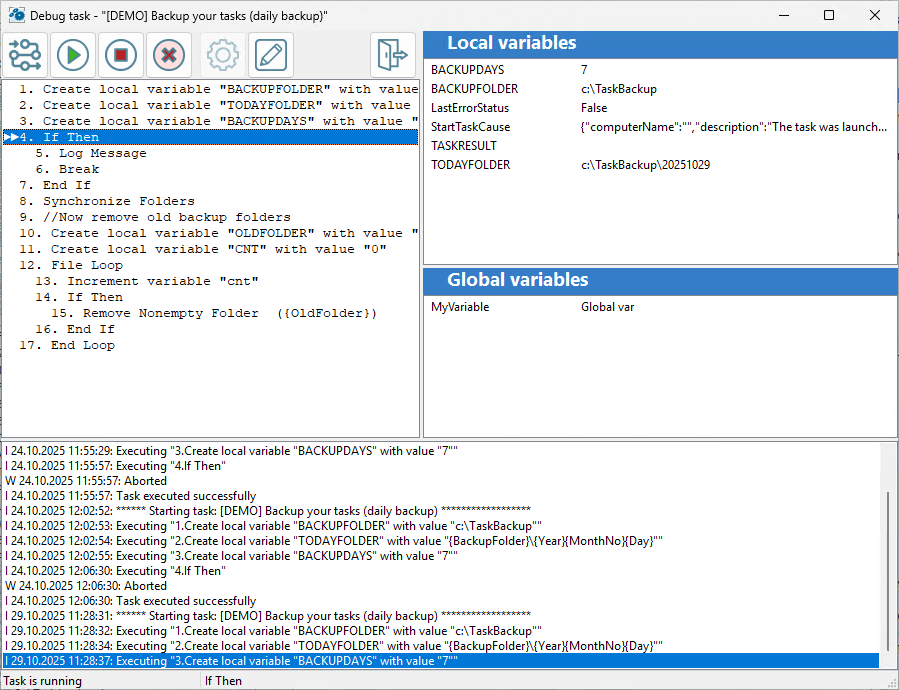
Task debugger
The debugger allows you to execute a task step by step and check the values of local and global variables. The debugger is launched directly from the task editor and allows you to quickly check and edit (if necessary) the step parameters or return to the task editor.
Please note that the debugger is only available for local tasks. If you need to debug a task on a remote computer, you will need to copy it to your local RoboTask.
![]() Step over (F8)
Step over (F8)
Execute one step and proceed to the next active step. The debugger skips inactive steps.
![]() Run (F9)
Run (F9)
Run the task until the nearest breakpoint. If no breakpoints are specified, the task will run until completion.
![]() Stop Task (F2)
Stop Task (F2)
Interrupt task execution
![]() Toggle breakpoint (F5)
Toggle breakpoint (F5)
Set or remove a breakpoint on the selected step
![]() Task parameters
Task parameters
If necessary, you can specify the required parameters before starting to debug the task. The specified parameters are saved until the next debugging session. This means that you do not need to re-enter the parameters if you need to debug the task again later.
Please note that it only makes sense to enter parameters before starting the task in the debugger.
![]() Step parameters
Step parameters
Clicking the "Step parameters" button (or double-clicking on step) loads the step editor. You can quickly view or correct the step parameters.
![]() Return to task editor
Return to task editor
Finish debugging and return to the task editor.
It is also recommended to output variable values to the task log for monitoring during task execution.
The task often does not work correctly because the variable contains the wrong value: empty or incorrect.
To ensure that the variables are filled in correctly, you can check their values before performing key actions.
![]() Related Topics
Related Topics